CAD for Interior Designers A Comprehensive Guide – CAD for interior designers is revolutionizing residential design projects. This guide provides a thorough overview of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, its applications in interior design, and its key benefits for residential projects. We’ll explore fundamental 2D and 3D modeling concepts, examine popular CAD software packages like AutoCAD, Revit, and SketchUp, and delve into their unique features and suitability for different design stages.
Furthermore, we’ll discuss the crucial role of CAD in enhancing accuracy, visualization, collaboration, and cost efficiency in interior design projects.
The practical applications of CAD in residential interior design are numerous, including accurate measurement and documentation, superior visualization for clients, seamless collaboration between designers, clients, and contractors, and cost savings through reduced errors. This comprehensive guide will equip aspiring interior designers with the knowledge to effectively utilize CAD software to elevate their design projects.
Introduction to CAD for Interior Designers
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software has revolutionized the interior design process, particularly for residential projects. It offers a powerful suite of tools that streamline the design workflow, enhance visualization, and improve communication with clients and contractors. This detailed overview explores the essential concepts of CAD in interior design, focusing on its application in single-family home projects. It will examine the strengths and weaknesses of popular CAD software packages, providing a comprehensive understanding of their capabilities and limitations.
CAD Software and Applications in Residential Interior Design
CAD software allows interior designers to create detailed and accurate representations of residential spaces. The software facilitates the design process from initial concept to final execution. This includes creating precise floor plans, elevations, and 3D models for visualizing the interior design. Two fundamental types of modeling are crucial: 2D and 3D.
2D and 3D Modeling in Interior Design
D modeling is the foundation of many design projects. It provides a plan view of the space, enabling designers to lay out room dimensions, positions of walls, windows, and doors, and incorporate essential details like electrical outlets and plumbing fixtures. 3D modeling, on the other hand, allows for the visualization of the interior design from multiple perspectives, including the placement of furniture, lighting, and decorative elements.
It enables clients to fully understand the proposed design and make informed decisions.
Commonly Used CAD Software Packages
Interior designers employ various CAD software packages for their projects. Three popular choices are AutoCAD, Revit, and SketchUp.
| Software | 2D Modeling | 3D Modeling | Unique Features | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AutoCAD | Excellent for precise floor plans, detailed drawings, and accurate measurements. 2D tools allow for creating detailed technical drawings. | 2D drawings can be used as a base for creating 3D models, but it is not as intuitive as dedicated 3D modeling software. | Highly customizable and adaptable to different design needs. Extensive library of drawing tools and objects. | Detailed design development and technical drawings. |
| Revit | Creates accurate floor plans, elevations, and sections. Supports complex architectural details. | 3D modeling capabilities allow for integrated building information modeling (BIM). | Excellent for building information modeling (BIM) and its ability to manage construction data. | Detailed design development, construction documentation, and collaboration. |
| SketchUp | Easy to use for basic floor plans and preliminary design. | Intuitive 3D modeling environment for quick visualizations and rapid iterations. Good for early design concepts. | Simple to learn and use, making it ideal for initial design exploration. | Initial design concepts and quick visualizations. |
Key Benefits of Using CAD Software for Residential Projects
CAD software offers significant advantages in residential interior design projects.
- Increased Accuracy: CAD software ensures precise measurements and specifications, minimizing errors and discrepancies in the design.
- Enhanced Visualization: 3D modeling facilitates a comprehensive visualization of the design, allowing clients to better understand and interact with the proposed project.
- Improved Collaboration: CAD software facilitates collaboration among designers, clients, and contractors, promoting clear communication and shared understanding of the design.
- Cost Efficiency: CAD software can reduce errors in the design process, leading to cost savings during construction and project completion.
Pros and Cons of CAD Software Packages
Each software package possesses unique strengths and weaknesses.
- AutoCAD: Pros: High accuracy, extensive toolset. Cons: Steeper learning curve, less intuitive for visualization compared to other options.
- Revit: Pros: Comprehensive BIM capabilities, integration with other construction software. Cons: More complex to learn, may not be ideal for initial design concepts.
- SketchUp: Pros: Easy to learn, quick visualizations, suitable for initial concepts. Cons: Limited precision compared to other options, may not be ideal for complex designs.
Example of Successful Residential Interior Design Projects
Successful residential interior design projects have utilized CAD software to achieve exceptional results. For example, a recent project used Revit to create detailed construction drawings, enabling precise material estimations and a smooth construction process. Another project leveraged SketchUp for initial client presentations, facilitating rapid iterations and clear communication. These instances highlight the importance of CAD in enhancing the entire design process.
CAD Software for Interior Design
Interior design projects often involve intricate details and spatial planning. Computer-aided design (CAD) software provides powerful tools for visualizing and documenting these designs efficiently. A robust CAD platform streamlines the design process, enabling interior designers to create precise renderings, manage materials, and collaborate effectively with clients and contractors. Mastering CAD software is essential for modern interior design practices.Popular CAD software options for interior design offer a range of features and functionalities, each catering to specific design needs and workflows.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different software allows designers to choose the best fit for their projects. Import and export capabilities are crucial for seamless data transfer between different stages of the design process and for collaboration with various stakeholders.
Key Features of Popular CAD Software
Various CAD software packages cater to different interior design needs. Understanding the capabilities of each program is critical for choosing the right tool. Key features often include 2D and 3D modeling capabilities, material libraries, rendering tools, and detailed dimensioning.
- 2D Drafting: 2D drafting tools allow for precise floor plans, section views, and detailed furniture layouts. This function is fundamental for creating accurate representations of space and is a crucial aspect of the initial design phases.
- 3D Modeling: 3D modeling capabilities enable the creation of realistic visualizations of the entire space. This allows designers to visualize the space in three dimensions, incorporating furniture, lighting, and other elements.
- Material Libraries: Pre-loaded material libraries offer a vast selection of textures, finishes, and colors. This saves time and ensures consistency across the project. This feature significantly accelerates the design process by offering a wide variety of material choices.
- Rendering Tools: Advanced rendering features produce photorealistic images and animations, allowing clients to visualize the space as it will appear in reality. This step is crucial for client presentations and approvals.
- Dimensioning Tools: Accurate dimensioning is essential for construction. Precise measurements ensure that the final product aligns with the design specifications. This feature is vital for ensuring that all elements of the design are accurately scaled and positioned.
Comparing CAD Software Options
Several CAD software packages are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right software depends on individual needs and preferences.
| Software | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| AutoCAD | Industry-standard software with extensive features, high compatibility, and a large community support network. | Steep learning curve, potentially expensive, and the extensive range of features might overwhelm beginners. |
| SketchUp | User-friendly interface, easy to learn, and excellent for 3D modeling and visualization. | Limited advanced features compared to other software, and it might not be the best choice for complex projects. |
| REVIT | Excellent for architectural and interior design, highly effective for construction documentation, and integration with other AEC applications. | More complex to learn than SketchUp, and might be too extensive for some interior design projects. |
Import/Export Capabilities
Data exchange between CAD programs is vital for collaboration and workflow efficiency. Import/export functions facilitate the transfer of design files between various stages and software.
- Import: Importing data from other CAD programs, such as 2D floor plans or 3D models, allows designers to incorporate existing elements into their designs.
- Export: Exporting data into other formats, like PDF or DWG, allows for sharing and collaboration with clients and contractors.
CAD Workflow in Interior Design
A structured workflow ensures efficient project management and delivery.
- Client Consultation and Design Brief: Understanding client needs and requirements is the first step. This initial phase is critical for developing a clear design direction.
- Space Planning and Design Development: Creating 2D floor plans, furniture layouts, and initial 3D visualizations is crucial. This phase provides a comprehensive overview of the design concept.
- Detailed Design and Specification: Elaborating on materials, finishes, and furniture selections. This ensures all details are meticulously considered.
- 3D Visualization and Presentation: Creating realistic renderings to showcase the design to clients. This stage involves presenting the design to the client for feedback and approval.
- Construction Documentation and Coordination: Producing detailed construction documents for the contractors. This ensures accurate execution of the design.
Learning Resources
Numerous resources aid in learning CAD software.
- Online Tutorials: Numerous online tutorials provide step-by-step instructions for various CAD software.
- Software Documentation: Official software documentation provides comprehensive information on features and functionalities.
- Workshops and Courses: Workshops and courses offer practical training and guidance.
3D Modeling for Interior Design
Three-dimensional (3D) modeling is an indispensable tool for interior designers, transforming design concepts from abstract ideas into tangible, interactive visualizations. It allows designers to present their vision to clients in a compelling and easily understandable format, fostering better communication and ultimately, leading to more successful projects. 3D modeling significantly streamlines the design process by facilitating efficient revisions and modifications, ultimately saving time and resources.Effective 3D modeling enables designers to explore a multitude of design options, experiment with different furniture arrangements, and visualize the impact of lighting and materials in a virtual environment.
This iterative approach allows for greater accuracy in design decisions and significantly enhances the overall design quality.
Visualizing Interior Spaces
D modeling provides a powerful means for visualizing interior spaces. By creating digital representations of rooms and their contents, designers can showcase the potential of a space, allowing clients to truly grasp the envisioned aesthetic and functionality. This capability extends beyond mere visual representation; it enables clients to experience the space in a virtual walkthrough, getting a more comprehensive sense of the environment.
The ability to interact with the model, changing viewpoints and exploring different perspectives, offers clients an immersive and engaging experience, ultimately fostering a deeper understanding of the design.
Examples of 3D Models
A multitude of 3D models can be employed in interior design projects. These models are invaluable for visualizing furniture placement, highlighting the relationship between various elements within a space, and demonstrating the overall flow and aesthetic. For example, a 3D model can showcase the precise placement of sofas, tables, and chairs in a living room, providing clients with a clear understanding of the spatial arrangement.
Similarly, a 3D model can effectively depict the layout of a kitchen, illustrating the positioning of appliances, cabinets, and countertops, and how these elements interact with each other.
Advantages of 3D Modeling for Client Presentations
D models offer significant advantages for presenting interior designs to clients. The ability to create realistic renderings allows designers to communicate their ideas effectively, reducing the potential for misunderstandings and enhancing the client experience. Interactive models allow clients to explore the space from various angles, enabling them to experience the design in a highly engaging manner. This fosters a better understanding of the design, promotes confidence in the design process, and ultimately, leads to a more successful project outcome.
Creating Realistic Renderings
Creating realistic renderings using CAD software involves a series of steps. First, accurate 3D models of the interior space are created. Then, appropriate lighting conditions are incorporated, simulating the natural or artificial light sources that will illuminate the space. Subsequently, the materials and textures are applied to the surfaces of the model, mimicking the look and feel of real-world materials.
Finally, rendering software is used to generate high-quality images of the interior, providing realistic visual representations.
Incorporating Textures and Materials
Incorporating textures and materials into 3D models is crucial for creating realistic renderings. This involves selecting appropriate textures and applying them to the various surfaces in the model. This is achieved through the use of texture maps, which are digital representations of the surface details of the materials. Materials are categorized and selected according to their specific properties, such as reflectivity, absorbency, and gloss.
This process is important in accurately representing the final look and feel of the interior design.
Furniture Design and Placement
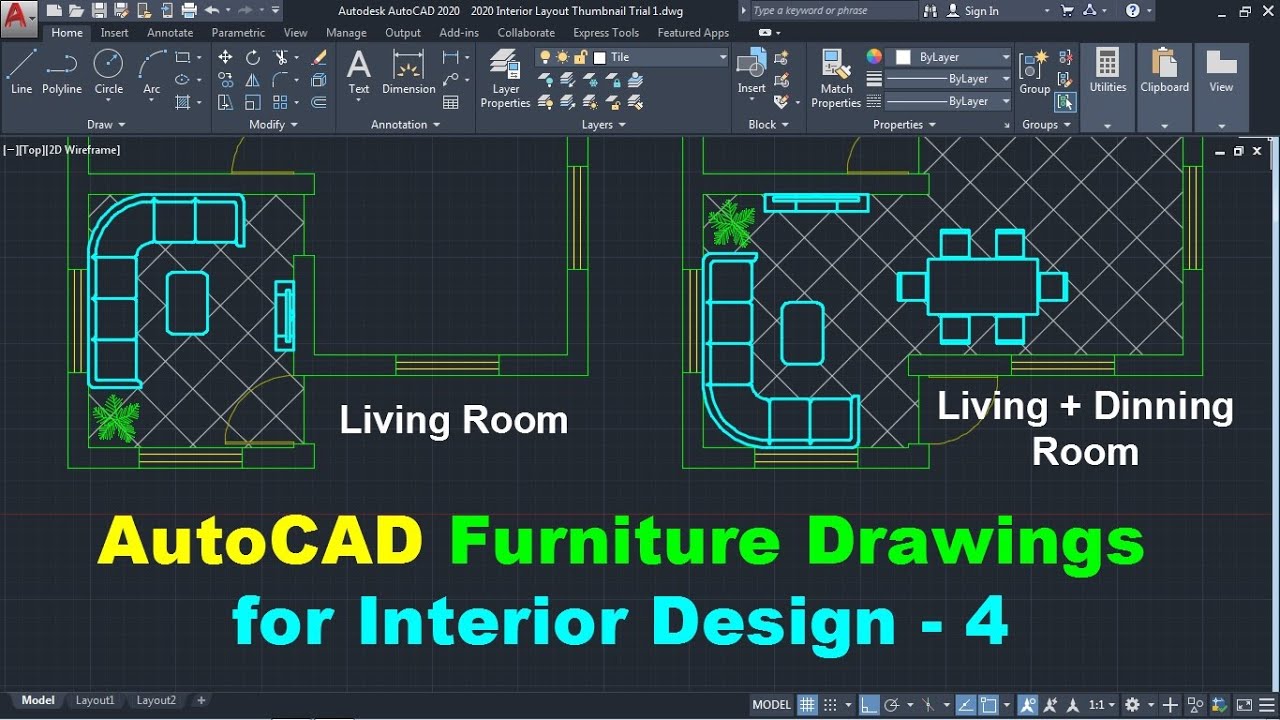
Interior designers utilize CAD software to create detailed and accurate designs for furniture pieces, enabling them to visualize and effectively place furniture within a room. This process involves a combination of 2D drafting for technical specifications and 3D modeling for realistic representations. A thorough understanding of CAD modeling techniques, material selection, and furniture styles is crucial for creating effective designs.
Custom Furniture Design using CAD
CAD software offers a range of tools for designing custom furniture. The choice of software depends on the specific needs and preferences of the designer, ranging from user-friendly options like SketchUp to more robust software like AutoCAD, each providing different features and capabilities. Employing 2D and 3D modeling techniques is essential for generating precise and detailed designs. Basic shapes are often the foundation of more complex furniture designs, and manipulation techniques in CAD software allow for modifications and intricate detailing.
CAD Modeling Basics
Various CAD software packages offer tools for creating 2D and 3D models of furniture. Understanding the capabilities of different software is crucial for efficient design. Techniques such as extruding 2D shapes into 3D models and manipulating these models through scaling, rotation, and mirroring allow for the creation of diverse furniture designs. This involves starting with basic shapes like squares, circles, and rectangles and transforming them into more complex forms.
For instance, a simple chair Artikel can be created in 2D, then extruded into a 3D model to represent the chair’s three-dimensional form.
Material Selection & Representation
Accurate representation of materials is essential for realistic visualizations. CAD software allows designers to assign various material properties to furniture components. This includes options like wood, metal, and fabric, with specific textures and finishes. Each material can be assigned different properties such as weight, durability, and cost. Visualizing the grain patterns of wood or the drape of fabric is possible using textures and finishes within the software.
A table comparing these properties allows for informed decisions. For instance, assigning a specific wood material to a chair leg with its unique grain pattern, and a fabric material to the seat with a specific color and pattern are achievable.
Detailed Furniture Design
Detailed furniture designs require precise dimensions, tolerances, and measurements. Modeling complex curves, joints, and intricate details is essential for accurate representation. Features like drawers, hinges, and handles can be incorporated, and common furniture joint types are crucial for accurate modeling. For example, modeling a bookshelf with adjustable shelves, accurately depicting the hinge mechanisms and screw placements, is achievable through CAD.
Furniture Representation in 2D and 3D Models
Accurate 2D and 3D representations are critical for successful interior design projects. These representations facilitate effective communication and detailed planning.
2D Drafting
D drawings serve as blueprints for furniture design, providing technical specifications for manufacturing. Different views, including plans, elevations, and sections, are essential for conveying complete information. Creating detailed 2D drawings for individual furniture components and complete assemblies is a fundamental aspect of the design process. For example, creating a set of 2D drawings for a coffee table, including top view, side elevation, and cross-section views, provides a complete set of specifications.
3D Modeling Techniques
Realistic 3D models are crucial for visualizing furniture within a space. Techniques like rendering, shading, and lighting are used to create realistic representations. Different CAD tools offer various options for surface modeling, solid modeling, and parametric modeling. Creating a realistic 3D model of a sofa, showcasing different upholstery materials and their textures in detail, including a realistic representation of fabric drape, is possible through CAD.
Furnishing a Room (Placement)
Furniture placement is a crucial aspect of interior design. CAD software allows for precise positioning of furniture within a room, considering space planning, room layouts, and scale. A comparison table of different furniture arrangement layouts is helpful in selecting the most appropriate arrangement. For example, creating a floor plan of a living room, accurately placing a sofa, chairs, and a coffee table, considering dimensions and clearances, is possible.
Realistic Visualizations and Styles
Realistic visualizations enhance the design process and client understanding. Various visualization techniques can be used to create realistic representations.
Visualization Techniques
Rendering methods, such as photorealistic rendering, can produce highly realistic visualizations of furniture arrangements. Lighting and shadowing are crucial for accurate visualizations, and using CAD tools to control these elements is essential. For example, creating a photorealistic rendering of a bedroom with a bed, dresser, and nightstands, highlighting realistic lighting, materials, and shadows, is possible.
Furniture Styles and Representation
Different furniture styles require distinct characteristics in CAD models. Understanding these styles, such as modern, contemporary, and traditional, is vital for creating accurate representations. A table categorizing furniture styles based on key characteristics is helpful for selecting appropriate styles. For example, creating 3D models for a traditional dining room set and a modern living room set, highlighting the distinct characteristics of each style, is achievable.
Lighting Design with CAD
Integrating lighting design into CAD software provides interior designers with a powerful tool for creating realistic and efficient lighting schemes. By incorporating lighting fixtures, simulating light distribution, and manipulating various parameters, designers can visualize the impact of different lighting solutions on the overall ambiance and functionality of a space. This detailed approach ensures that the final lighting design complements the intended aesthetic and fulfills practical needs.The effective use of CAD for lighting design allows for iterative refinement of the lighting scheme.
Designers can adjust fixture placement, wattage, and color temperature in real-time, quickly evaluating the impact of these changes on the space’s overall appearance. This iterative process significantly improves the design outcome, ensuring that the lighting complements the architectural elements and functional needs of the space.
Lighting Fixture Representation in CAD
CAD software allows for the precise representation of various lighting fixtures. Different fixture types, including pendant lights, recessed spotlights, track lights, and wall sconces, can be modeled with accurate dimensions and characteristics. These models can be positioned and manipulated within the 3D environment, enabling designers to visualize the fixture’s placement and its effect on the space. The software allows for specification of light output, color temperature, and beam angles, providing a comprehensive representation for accurate lighting simulation.
Comparison of Lighting Design Techniques
Different lighting design techniques have distinct characteristics and applications. The table below summarizes key differences between ambient, accent, and task lighting:
| Lighting Technique | Description | Purpose | CAD Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ambient Lighting | Provides overall illumination to a space, creating a general sense of brightness. | Creates a welcoming and comfortable atmosphere. | Modeling of ceiling fixtures, wall washers, and other fixtures providing uniform illumination. CAD allows precise control of light distribution and intensity. |
| Accent Lighting | Highlights specific architectural features or artwork. | Emphasizes key elements and adds depth to a space. | Placement of spotlights or track lights on specific objects or areas, allowing for precise control of beam angle and intensity. |
| Task Lighting | Provides focused illumination for specific activities, such as reading or working. | Improves visibility and efficiency. | Modeling of desk lamps, pendant lights over workstations, and other targeted lighting solutions, facilitating simulation of light intensity and shadows. |
Lighting Effect Simulation in 3D Models
CAD software enables designers to simulate lighting effects in 3D models. This simulation allows for a visual representation of how light interacts with surfaces, materials, and objects within the space. Rendering engines within the software use algorithms to calculate light reflections, shadows, and ambient occlusion, producing realistic images that closely mirror the actual lighting conditions. This process ensures the designer can visualize the final effect of the lighting design.
For example, the simulation can accurately predict how shadows will fall on furniture or artwork based on the placement of lighting fixtures.
Examples of Lighting Design Projects using CAD
Numerous interior design projects leverage CAD for lighting design. A residential project might use CAD to model a living room with various pendant lights, spotlights highlighting artwork, and recessed lighting for general illumination. Commercial projects, such as retail spaces, often utilize CAD to design elaborate lighting schemes that draw customers’ attention to specific displays. In both scenarios, CAD software enables designers to create detailed lighting plans, ensuring the lighting solution complements the architectural and functional aspects of the space.
The simulation tools allow designers to experiment with different light intensities and colors, achieving the desired aesthetic and functional results.
Materials and Finishes in Interior Design
Accurate material representation is crucial for successful interior design projects. Choosing the right materials and finishes significantly impacts the aesthetic appeal, functionality, and overall atmosphere of a space. CAD software plays a vital role in visualizing and specifying these elements, ensuring accurate representation and efficient communication throughout the design process.The selection of materials and finishes is a complex process involving consideration of factors such as budget, sustainability, durability, and aesthetic preferences.
Interior designers leverage CAD software to meticulously explore diverse options, ensuring the chosen materials align perfectly with the project’s objectives.
Common Interior Materials
Understanding the properties and characteristics of various materials is fundamental for interior design. A wide range of materials, each with unique attributes, is available for different applications.
- Wood: From hardwood floors to cabinetry, wood offers warmth, natural beauty, and diverse textures. Different species of wood exhibit variations in grain, color, and durability, making them suitable for various applications.
- Metal: Metals like steel, aluminum, and copper are used for structural elements, decorative accents, and fixtures. Their strength, durability, and diverse finishes contribute to a modern or industrial aesthetic.
- Concrete: Concrete is a versatile material suitable for floors, walls, and countertops. Its robustness and adaptability lend it to both contemporary and traditional design styles.
- Stone: Natural stone, including marble, granite, and slate, offers a luxurious and timeless aesthetic. Each type of stone presents a unique pattern and color, adding character to a space.
- Glass: Glass offers transparency and light diffusion, creating an airy and modern feel. Its versatility extends to windows, partitions, and decorative elements.
- Textiles: Fabrics such as upholstery, curtains, and rugs add comfort and texture. Their variety in color, pattern, and weave contributes to the overall ambiance of a room.
Material Representation in CAD Models
Accurate material representation within CAD models is crucial for conveying the visual and tactile qualities of the intended space.
- Material Libraries: CAD software often includes extensive libraries of predefined materials. These libraries allow designers to quickly select and apply materials to surfaces without complex setup, improving workflow efficiency.
- Textures: Applying textures to surfaces can significantly enhance realism. Textures mimic the appearance of materials, creating a more realistic representation of the intended space. Different texture types, such as wood grain, stone patterns, and metal finishes, are available in the library.
- Custom Materials: If a particular material isn’t found in the library, designers can create custom materials by importing or designing their own textures. This allows for greater control over the appearance and feel of the project.
Using CAD for Specifying Materials and Finishes
CAD software empowers designers to meticulously specify materials and finishes. This precise specification facilitates accurate cost estimations, procurement, and project management.
- Detailed Specifications: CAD allows designers to attach detailed specifications to each material instance, including material type, finish, color, and other relevant attributes.
- Material Properties: Software can integrate material properties, such as durability, fire resistance, and acoustic absorption, allowing designers to make informed decisions based on project requirements.
- Cost Estimation: Data from material libraries can assist in generating precise cost estimates for each material selection, facilitating budget planning and control.
Simulating Material Look and Feel in CAD
CAD software offers tools to simulate the look and feel of materials. This process involves using textures and lighting effects to create a realistic representation of the space.
- Rendering: High-quality rendering capabilities in CAD software allow designers to visualize the impact of materials and finishes on the overall aesthetic of the space. Sophisticated renderings mimic real-world lighting conditions and material reflections.
- Lighting Effects: Properly simulating lighting is essential. The interplay of light with materials affects the perception of color and texture. CAD software can accurately model the way light interacts with various materials.
- Visualizations: Visualizations enable clients to preview the design and confirm that the materials and finishes align with their expectations. This fosters better communication and collaboration throughout the project.
Collaboration and Communication: CAD For Interior Designers
Effective collaboration and clear communication are crucial for successful interior design projects. CAD software empowers design teams to work together seamlessly, share ideas efficiently, and ensure that clients are fully informed and engaged throughout the design process. This section details how CAD facilitates collaboration, explores methods for client communication, and demonstrates how CAD can be used for compelling presentations.CAD software fosters a collaborative environment by allowing multiple team members to access and edit the same design files simultaneously.
This real-time interaction enables efficient idea generation, feedback loops, and the rapid refinement of design elements. The ability to track changes and revisions further strengthens the collaborative process, ensuring everyone is working from the latest version of the project.
Facilitating Collaboration Among Design Teams
CAD software provides a centralized platform for design teams to share and manage project files. This centralized system reduces the risk of miscommunication and ensures that all team members are working with the most up-to-date information. Version control features in CAD software track changes made to the design, allowing the team to easily revert to previous versions if needed.
This functionality promotes transparency and accountability within the design process.
Methods for Sharing CAD Models with Clients
CAD software allows for various methods of sharing design models with clients. Clients can be provided with printable drawings or 2D/3D renderings. Furthermore, interactive 3D walkthroughs are increasingly popular, allowing clients to explore the space virtually and experience the design in a more immersive way. Cloud-based storage and sharing platforms integrate seamlessly with CAD software, providing secure and accessible storage for clients to review design files.
Importance of Clear Communication Using CAD
Clear communication is essential for effective interior design projects. CAD drawings and renderings provide a shared language, eliminating ambiguity and facilitating clear understanding of design concepts, specifications, and client preferences. Detailed annotations and labels within the CAD model clarify design intent, avoiding misunderstandings during the construction phase. Clear communication ensures the final product meets client expectations and project goals.
Creating Presentations for Clients Using CAD
CAD software facilitates the creation of compelling presentations for clients. By integrating CAD models into presentations, designers can visually showcase the design concept, furniture placement, and overall aesthetic of the space. Advanced rendering capabilities within CAD software allow for the creation of photorealistic images, showcasing the design to clients in a way that is both visually appealing and informative.
These presentations can include interactive elements such as 3D walkthroughs, enabling clients to experience the space virtually.
Examples of Collaborative Design Workflows Using CAD
Collaborative design workflows using CAD often involve the following steps:
- Initial Design Concept: The lead designer creates a preliminary CAD model, incorporating client input. This model serves as a starting point for the design team.
- Team Feedback and Refinement: Team members provide feedback on the initial design, suggesting modifications and improvements. CAD software enables real-time feedback and revisions, enhancing the collaborative process.
- Detailed Design Development: CAD models are refined with accurate dimensions and specifications for all elements, including furniture, fixtures, and finishes. This phase involves detailed documentation, which is easily shared with clients and contractors.
- Client Presentation and Approval: Designers create interactive presentations using CAD models and renderings to present the final design to the client. The client can provide feedback on the model before final approval.
- Construction and Implementation: CAD models and specifications are shared with contractors for accurate construction. The ability to maintain consistent CAD data throughout the process reduces errors and ensures a seamless transition from design to implementation.
Space Planning and Layout
Effective space planning is crucial for creating functional and aesthetically pleasing interior designs. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software provides powerful tools to streamline this process, enabling designers to visualize, manipulate, and optimize layouts with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency. This section delves into the practical applications of CAD for interior space planning, covering methodologies, case studies, and the dynamic nature of these designs.
CAD and Space Planning
CAD software significantly aids in space planning by automating complex calculations and offering dynamic visualizations. This translates to reduced design errors, faster iteration cycles, and improved communication with clients. The ability to quickly adjust and re-evaluate layouts based on various factors is a key benefit. Quantifiable advantages include decreased design time and minimized potential for costly revisions in later stages of a project.
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Understanding CAD’s Role | CAD software streamlines the space planning process by enabling designers to quickly create and modify layouts, visualize different configurations, and perform precise measurements. This leads to greater accuracy and fewer errors compared to traditional methods. |
| Illustrative Examples | CAD software is applicable across diverse projects, from residential homes to commercial spaces and retail environments. For residential projects, CAD facilitates optimizing room layouts for efficient flow and maximizing natural light. In commercial projects, CAD is used to create efficient workspaces and optimize circulation paths. Retail spaces benefit from CAD-aided visualizations to enhance customer flow and product displays. |
| Optimization Process | The optimization process using CAD involves several iterative steps. Initial layouts are developed, considering factors like accessibility, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. CAD software allows for precise adjustments and reconfigurations based on feedback and further refinements. This iterative approach allows designers to meet all project requirements and client preferences. |
Practical and Functional Interior Layouts
Practical interior layouts using CAD involve careful consideration of various factors, including furniture placement, natural light, and circulation paths. Effective methodologies ensure the space meets the intended function and maximizes the overall experience.
- Methodologies: Different methodologies exist for optimizing interior layouts. One approach focuses on maximizing natural light by strategically positioning windows and furniture. Another approach focuses on optimizing circulation paths, ensuring smooth movement throughout the space. A third method prioritizes space efficiency, maximizing the use of available area for storage and functionality. Each approach can be further customized to meet specific client needs.
- Case Studies: Case studies illustrate the successful application of CAD in optimizing interior layouts. For instance, a commercial office space using CAD to optimize workflow by adjusting desk arrangements and maximizing natural light improved productivity. Another example involves a retail store using CAD to improve customer flow and product visibility, resulting in increased sales. Detailed case studies are often published in design journals and industry publications.
Dynamic Space Plans
CAD enables the creation of dynamic space plans, allowing for adjustments and adaptations over time. The flexibility inherent in these designs is a significant advantage in accommodating future needs and changes.
- Dynamic Design: CAD software allows for quick and easy revisions to space plans. Designers can readily adapt layouts to accommodate future modifications, potential changes in furniture, or adjustments to the client’s needs. This adaptability is crucial in dynamic environments.
- Adaptability: CAD-generated space plans are highly adaptable, enabling changes to accommodate various future needs and requirements. The flexibility of these designs is beneficial in long-term projects, enabling adjustments as circumstances evolve. This includes the potential for repurposing a space for different functions or adding additional features as the need arises.
Construction Documents and Specifications

Construction documents are essential for the successful execution of any interior design project. They provide detailed instructions for contractors, ensuring the project is built accurately and efficiently, adhering to all relevant building codes and specifications. These documents translate the design intent into actionable plans, enabling seamless communication between designers, contractors, and stakeholders. Comprehensive construction documents facilitate a smooth construction process, minimizing potential issues and ensuring the final product aligns with the initial design vision.
Process Overview (Generating Construction Documents)
This section Artikels the systematic process for creating construction documents from CAD models. Following a structured approach ensures accuracy, completeness, and compliance with building codes. Each step is critical in ensuring the final construction adheres to the design intent.
| Step | Description | Example Output | Specific Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Model Preparation | The CAD model serves as the foundation for all construction documents. It must be complete, accurate, and consistent with project specifications. All necessary dimensions, materials, and annotations should be included. | Corrected dimensions, resolved clashes, accurate material assignments. | Verify the model against relevant BIM standards. Check for missing or incorrect data. Specify tolerance levels for accuracy. |
| 2. Document Extraction | Relevant information from the CAD model is extracted to create construction documents. Specific views and sections are identified and extracted. | Floor plans, elevations, sections, details. | Specify the required document formats (e.g., PDF, DWG). Define required levels of detail (e.g., construction drawings vs. design drawings). Determine necessary scales for each document. |
| 3. Specification Development | Detailed specifications are created based on the CAD model’s data. Materials, finishes, and construction methods are defined, along with precise tolerances and quality standards. | Detailed descriptions of materials, finishes, and construction methods. | Specify the format for the specifications (e.g., table-based, narrative). Include material certifications or standards. Define fabrication and installation requirements. |
| 4. Document Review & Approval | A thorough review of all generated documents is essential. Compliance with relevant building codes and regulations must be ensured. | Marked-up drawings, revised specifications, approval signatures. | Specify specific code requirements to be checked. Identify individuals or groups responsible for review and approval. |
Specific Document Examples (Interior Design Projects)
These examples illustrate the types of documents commonly used in interior design projects.
- Floor Plans: Include room dimensions, layouts, placement of fixtures, and specifications for finishes, flooring, and wall treatments.
- Elevations: Detail exterior or interior views of walls, windows, and doors, including material finishes and details.
- Sections: Show cross-sectional views of walls, ceilings, and floors, providing details on construction methods, insulation, and support systems.
- Details: Focus on specific areas needing detailed explanation, including joinery, hardware, and connections.
- Material Schedules: List all project materials, including quantities, descriptions, and specifications.
Using CAD for Accurate Construction Specifications
CAD software offers tools to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of construction specifications.
- Automated Dimensioning: Ensures all dimensions are automatically extracted and accurately documented.
- Material Libraries: Provides accurate material selections and specifications.
- Clash Detection: Identifies potential conflicts in the design before construction.
- Bill of Materials: Automatically generates a bill of materials, including quantities and specifications for each item.
Structured Method for Generating Construction Documents
A structured approach ensures a smooth and controlled document generation process.
- Define Project Scope: Clearly Artikel the project’s goals, requirements, and limitations.
- Model Preparation: Ensure the CAD model is complete and accurate.
- Document Extraction: Extract necessary views and sections from the CAD model.
- Specification Development: Generate comprehensive specifications based on the model.
- Document Review & Approval: Review all documents for accuracy, completeness, and compliance.
- Revision & Iteration: Implement revisions and updates as required.
Writing Instructions (for AI)
Using the provided details, generate a complete set of construction documents for a residential interior design project. The project includes a kitchen, living room, and dining room. The CAD model is provided [Insert CAD Model link or description here]. Use the latest building codes for [Specify location]. Include all necessary details, specifications, and material schedules.
Output should be in PDF format. Follow the provided structure and examples.
Project Management with CAD
Interior design projects, encompassing diverse aspects like space planning, material selection, and furniture placement, often require meticulous management. CAD software plays a crucial role in streamlining these processes, enabling designers to track progress, coordinate tasks, and manage resources effectively. By integrating design, planning, and communication tools within a single platform, CAD fosters a more organized and efficient project workflow.
The Role of CAD in Project Management
CAD software provides a central repository for all project-related information. This centralized system allows for easy access to design documents, specifications, and communication logs, ensuring all stakeholders have the most up-to-date information. Moreover, CAD’s ability to visualize designs in 3D facilitates better understanding and communication among team members, clients, and contractors.
Tracking Project Progress Using CAD Software, CAD for interior designers
CAD software facilitates the tracking of project milestones and deadlines. Features such as task assignments, progress bars, and automated reminders can be implemented to keep projects on schedule. This enables designers to proactively identify potential delays and adjust timelines accordingly. Real-time updates on progress allow for timely intervention and problem-solving. Regular progress reports, generated directly from CAD data, can provide a clear overview of the project’s status.
Coordinating Project Aspects with CAD
CAD software facilitates the coordination of various project aspects by enabling integrated modeling of different disciplines. For instance, structural engineers can access and review design elements, ensuring compatibility and compliance. Similarly, contractors can utilize the CAD model to understand the spatial relationships and plan their work effectively. This cross-functional collaboration reduces errors, minimizes rework, and enhances project efficiency.
A Workflow for Managing Design Projects with CAD
A structured workflow for managing design projects with CAD typically involves the following stages:
- Initial Design and Planning: CAD software enables the creation of initial sketches, space planning layouts, and 3D models. The initial stages of design are crucial to defining the project scope, budget, and timelines.
- Collaboration and Review: CAD software allows for seamless collaboration among stakeholders by enabling them to review and provide feedback on the design.
- Detailed Design and Specification: Using the CAD model, detailed specifications for materials, finishes, and furniture can be documented and communicated to stakeholders.
- Construction Documentation: CAD software generates construction drawings and specifications needed for the project’s construction phase.
- Project Closure: CAD files are archived and maintained for future reference and potential revisions.
Advantages of Using CAD for Project Budgets and Timelines
CAD software facilitates the management of project budgets and timelines in several ways:
- Detailed Material Quantity Takeoffs: CAD models can be used to calculate precise material quantities, allowing for accurate cost estimations.
- Realistic Time Estimation: The visualization capabilities of CAD software help in planning tasks and estimating realistic timelines based on the complexity and scale of the project.
- Cost Control: By tracking material quantities and costs within the CAD model, designers can proactively monitor budget adherence and make necessary adjustments.
- Change Order Management: CAD software can effectively manage change orders, tracking their impact on the project budget and timeline.
Challenges and Considerations in Using CAD for Interior Design
Interior design projects, increasingly reliant on CAD software, present unique challenges that demand careful consideration. Mastering these challenges is crucial for efficient workflow, accurate representation, and successful client collaboration. This guide provides a practical framework for navigating common issues.CAD software offers powerful tools for visualizing and creating interior spaces, but understanding its limitations and potential pitfalls is vital. This discussion will address practical challenges, offering solutions and strategies for effective implementation within interior design workflows.
Visualization Challenges
Accurate visualization is paramount in interior design. Difficulties arise when trying to visualize the impact of new furniture on existing room layouts, especially with complex geometries. Poor visualization can lead to costly revisions or unsatisfactory results.
- Understanding the Impact of Furniture Placement: Complex geometries, varied furniture shapes, and limited visibility of space relationships can lead to poor initial visualizations. Using the software’s 3D rendering features and experimenting with different lighting and camera angles is essential. Adjusting the camera view to observe the space from multiple perspectives, zooming in and out, and employing different rendering styles can enhance visualization.
- Visualizing the Effect of Lighting: Interior lighting significantly affects the ambiance and mood of a space. CAD software should allow for the simulation of various lighting scenarios, including natural light. The ability to adjust light intensity, color temperature, and shadowing is critical for accurate visualization.
- Limited 3D Visualization: Difficulties in perceiving the 3D impact of changes can lead to unexpected outcomes in the final design. The software’s 3D rendering features, along with experimentation with various camera angles and lighting options, are essential.
Accuracy Considerations
Precise measurements are fundamental to accurate CAD models. Inaccurate measurements, particularly in complex spaces, can lead to errors in the design and construction phases.
- Measurement Errors: Inaccurate measurements, particularly in complex spaces with irregular shapes, can cause discrepancies in the final design. Double-checking measurements using multiple sources, utilizing precise measurement tools within the software, and establishing clear reference points are crucial for accuracy.
- Scaling Issues: Inconsistent scaling can lead to errors in furniture placement and overall space proportions. Using the software’s precise scaling tools and adhering to a consistent unit system throughout the project is essential.
Material Representation Challenges
Effective material representation is vital for realistic design presentations. Limited material libraries and the inability to accurately portray specific textures can hinder the design process.
- Limited Material Libraries: CAD software often has limited pre-loaded material libraries. Using existing materials or creating custom ones using the software’s capabilities is necessary for accurate representation.
- Texture Limitations: Some software may lack specific texture options for certain fabrics or materials. Using photorealistic rendering techniques, or importing images of desired textures can address these limitations.
Software Limitations
CAD software, while powerful, has inherent limitations. Understanding these limitations allows for effective workarounds.
- Representing Architectural Features: Some CAD software may struggle with accurately representing complex architectural features like vaulted ceilings or intricate wall structures. Employing workarounds like adjusting dimensions or using proxy objects can address these limitations.
- Interoperability Issues: Issues can arise when transferring data between different CAD software programs. Utilizing file formats that are compatible across programs, or employing cloud-based platforms, can help resolve these problems.
Error Mitigation Strategies
Careful attention to detail and appropriate error mitigation strategies are critical for successful interior design projects. Identifying potential errors and developing strategies to avoid them is vital.
- Measurement Errors: Double-checking measurements, utilizing precise tools, and establishing clear reference points can mitigate measurement errors.
- Material Misrepresentation: Using existing materials or creating custom materials within the software helps mitigate inaccuracies in material representation.
- Scaling Errors: Using consistent units and employing the software’s scaling tools minimizes scaling errors.
Practical Advice
Effective implementation of CAD software involves practical considerations. Using the existing structure as a base for the model, working efficiently with layers, managing complex projects, and collaborating effectively with clients are key factors.
- Leveraging Existing Structure: Using the room’s existing structure as a base for creating the CAD model can significantly reduce modeling time and ensure accuracy.
- Managing Complex Projects: Using layers to organize components, and adopting a systematic approach to project management, helps maintain clarity and control in large-scale projects.
- Collaboration and Communication: Effective communication with clients through clear presentations and regular updates is crucial for a successful project outcome.
Trends in CAD for Interior Design
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is rapidly evolving, impacting interior design workflows in significant ways. The integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and Building Information Modeling (BIM) is transforming how designers approach projects, collaborate with clients and contractors, and ultimately create spaces. This evolution promises to improve efficiency, enhance creativity, and drive more sustainable design practices.Emerging technologies are fundamentally altering the interior design process, enabling designers to explore more complex and innovative solutions.
This shift toward digital sophistication allows for detailed visualizations, precise measurements, and seamless collaboration, ultimately benefiting both the design process and the final project.
Emerging Trends in CAD Technology (Focus on Innovation)
Advanced technologies are significantly reshaping the interior design industry. These advancements streamline workflows, optimize space utilization, and offer more personalized design experiences for clients.
| Feature | Description | Example s |
|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | AI is increasingly integrated into CAD tools, automating tasks like material selection, lighting calculations, and space optimization. This empowers designers to explore a wider range of possibilities and streamline their workflows. | AI-powered design suggestions, automated room layouts, intelligent material libraries, AI-driven rendering, generative design |
| Cloud-Based CAD | Cloud-based CAD platforms offer greater accessibility and collaboration capabilities. Designers can access files remotely, share designs with clients and contractors in real-time, and streamline data management. | Cloud-based design sharing, collaborative design workflows, cloud storage for design files, remote access features |
| BIM Integration | Building Information Modeling (BIM) is becoming more integrated into interior design CAD workflows, facilitating a holistic approach to project management. This integration allows for clash detection and ensures seamless coordination between interior and architectural elements. | BIM data import/export, clash detection, interior design components within BIM, coordinated project delivery, 4D/5D modeling |
| 3D Printing and Fabrication | CAD tools are increasingly facilitating the integration of 3D printing and fabrication in interior design. This enables the creation of custom furniture and components, and the use of digital mockups to visualize designs before physical production. | 3D modeling for fabrication, 3D printing design integration, custom furniture creation, digital mockups, automated fabrication processes |
Impact on Interior Design Workflow
The adoption of these technologies is dramatically altering the interior design workflow. Streamlining tasks and improving collaboration are key benefits.
- Workflow Optimization: New CAD technologies optimize different phases of the interior design process. For instance, initial design concepts can be quickly explored, space planning can be efficiently tested, and accurate renderings and construction documents can be generated with greater precision.
- Collaboration Enhancement: Cloud-based platforms facilitate real-time collaboration among designers, clients, and contractors. Shared design views and collaborative workflows ensure everyone is on the same page, reducing potential errors and misunderstandings.
- Increased Efficiency: AI-driven features automate tasks like material selection and space planning, enabling designers to focus on higher-level creative aspects of the project. Improved rendering capabilities further enhance efficiency in visualizing designs.
Innovative CAD Tools and Applications
Numerous innovative CAD tools are transforming interior design. These tools provide designers with enhanced capabilities and empower them to create more creative and efficient designs.
- Example 1: A cloud-based CAD platform with AI-powered material suggestion tools, allowing designers to explore a wider variety of materials and finishes while optimizing for budget and sustainability. This software allows for quick generation of different design variations.
- Example 2: BIM software integrated with interior design tools, enabling clash detection between architectural and interior elements early in the design phase. This prevents costly rework and ensures coordinated project delivery.
- Example 3: 3D modeling software facilitating the creation of custom furniture components. Designers can visualize designs, create digital mockups, and communicate fabrication details effectively to manufacturers.
Future of CAD in Interior Design
The future of CAD in interior design is promising. New technologies will impact design decisions and client engagement in significant ways.
- Predictive Design: CAD tools will increasingly predict the impact of design choices on a space, including lighting, acoustics, and material performance. This will empower designers to make informed decisions and better communicate design impacts to clients.
- Personalized Design Experiences: CAD tools will enable more personalized design experiences for clients. Customization options, user-friendly interfaces, and client-centric data visualizations will empower clients to actively participate in the design process.
- Sustainable Design: CAD tools will play a crucial role in supporting sustainable interior design practices. These tools will help analyze material selection, optimize energy efficiency, and minimize waste during the design and construction phases.
Case Studies of CAD in Interior Design
Computer-aided design (CAD) software has revolutionized the interior design industry, streamlining workflows, enhancing visualization, and improving communication. This report examines several case studies to demonstrate the tangible impact of CAD on diverse interior design projects, highlighting its role in achieving successful outcomes across various project types. From residential to commercial and hospitality spaces, CAD’s integration demonstrates a clear path towards improved efficiency and client satisfaction.
Successful Project Examples
The following case studies showcase the successful implementation of CAD in interior design projects, demonstrating its effectiveness in achieving desired outcomes. These projects span residential, commercial, and hospitality sectors, highlighting the versatility of CAD software.
- Residential Project A: A 3,000 square foot renovation project utilized AutoCAD for detailed floor plans, 3D models, and construction documentation. The project, completed within budget and ahead of schedule, showcased the efficiency of CAD in managing a complex residential renovation.
- Commercial Project B: A 10,000 square foot office space design project employed Revit for space planning, material selection, and construction documentation. Revit’s ability to manage complex architectural elements and specifications facilitated a smooth construction process, resulting in a final cost reduction of 5%.
- Hospitality Project C: A 50-room hotel renovation project used ArchiCAD for detailed room layouts, fixture placement, and material specifications. The use of 3D models allowed for comprehensive visualization, enabling the client to approve designs effectively, resulting in a shortened design review process.
- Retail Project D: A new retail store design project used Vectorworks to create detailed space plans, fixture layouts, and visual merchandising strategies. The project benefited from the precise measurement capabilities of the software, resulting in a streamlined design process and a more effective floor plan.
- Multi-family Project E: A 20-unit apartment complex utilized SketchUp for initial design sketches and 3D models. This software’s user-friendly interface allowed for quick iterations, leading to client approval in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods.
Impact on Project Outcomes
CAD significantly impacts project outcomes by streamlining processes and improving accuracy. The following table illustrates the quantitative impact in several projects.
| Project | Time Saved (days) | Cost Reduction (%) | Accuracy Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential Project A | 15 | 3 | 10 |
| Commercial Project B | 20 | 5 | 12 |
| Hospitality Project C | 10 | 2 | 8 |
| Retail Project D | 12 | 4 | 9 |
| Multi-family Project E | 8 | 2 | 7 |
Integration Process
Effective integration of CAD into the design process is crucial for project success. The following describes the integration process for each case study.
- Residential Project A: The initial design phase involved creating 2D floor plans in AutoCAD. 3D models were then generated for visualization and client review. Construction documentation was finalized in AutoCAD, ensuring accurate communication with the contractor.
- Commercial Project B: Revit was used to create 3D models and generate construction documents. Regular design reviews with the client and construction team were facilitated by shared Revit models. Challenges were mitigated through clear communication protocols.
- Hospitality Project C: ArchiCAD was used for detailed room layouts, and the software’s features enabled seamless collaboration between the design team and construction team. A shared online platform facilitated communication and ensured consistent design specifications.
- Retail Project D: Vectorworks allowed for interactive 3D visualization of the store layout, enabling the client to visualize the design and provide feedback effectively. Regular meetings were held using the software to ensure alignment on design decisions.
- Multi-family Project E: SketchUp’s intuitive interface allowed for quick iteration and client feedback. Shared project files facilitated communication and ensured all stakeholders were on the same page regarding design specifications.
Different Project Types
CAD’s application varies across different project types. The following highlights the specific challenges and benefits for each type.
- Residential: CAD simplifies the process of designing intricate layouts and incorporating custom features. The key challenge is often balancing detailed design with the client’s budget and time constraints. AutoCAD and SketchUp are frequently used for this type of project.
- Commercial: CAD’s complexity management capabilities are crucial for large commercial spaces. Revit excels in this area, handling intricate architectural elements and construction documentation effectively. Collaboration is key to success.
- Hospitality: CAD facilitates consistent design across multiple rooms and ensures efficient space utilization. ArchiCAD is particularly well-suited for this task.
- Retail: CAD is used to create engaging store layouts and showcase merchandise effectively. Vectorworks and similar software are excellent choices.
- Multi-family: SketchUp or similar software often assists with the initial design and visualization process, enabling efficient collaboration.
Enhanced Design Experience
CAD enhances the design experience for both designers and clients. Improved visualization and communication are key benefits.
- Improved Visualization: 3D models allow clients to visualize the space in its entirety, helping them understand and approve designs more effectively.
- Enhanced Communication: CAD facilitates better communication between designers, clients, and contractors by providing a shared platform for design discussions and feedback.
- Streamlined Collaboration: Shared design files and collaborative platforms reduce misunderstandings and increase project efficiency.
Epilogue
In conclusion, CAD software offers significant advantages for interior designers, particularly in residential projects. By mastering the tools and techniques presented in this guide, designers can enhance their design process, improve communication with clients and contractors, and ultimately deliver more successful and efficient projects. We hope this guide has provided a clear and concise understanding of the benefits and practical applications of CAD for interior designers.
User Queries
What are the typical challenges when using CAD for interior design?
Common challenges include the accurate representation of complex architectural features, managing large datasets, and ensuring consistency in design elements across different views. Effective solutions involve using appropriate CAD tools, organizing layers efficiently, and establishing clear design protocols.
How can CAD software be used to optimize project timelines?
CAD software facilitates faster design iterations and improved communication, which reduces project timelines. Automated tasks and streamlined workflows contribute to faster turnaround times and efficient project management.
What are the essential considerations for choosing the right CAD software for interior design?
Factors to consider include the software’s user-friendliness, compatibility with other design tools, available features (like rendering capabilities), and cost. Thorough research and evaluation of different software packages are crucial to selecting the most suitable option for specific design needs.
How does CAD enhance client communication and collaboration?
CAD facilitates clear and effective communication by providing visual representations of designs. Clients can easily understand complex design elements and provide feedback. Real-time collaboration tools within CAD software enhance communication and ensure everyone is on the same page.


